
 01Purpose and Conditions
01Purpose and Conditions 02Working Medium
02Working Medium 03Fluid Requirements
03Fluid Requirements 04Size and Connection
04Size and Connection 05Other Considerations
05Other ConsiderationsChoosing the right valve means understanding the different types and how they work inside.
globe valve, regulating valve or safety valve.
gate valve, ball valve, butterfly valve, etc.
valve body, valve stem, valve disc and sealing surface, all made of suitable materials.
manual, electric, hydraulic or pneumatic operation.
The length and height of the valve.
Flange, threaded or welded connection.
Made by different methods such as welding or integrated into the valve body.
Rotating or rising stem options.
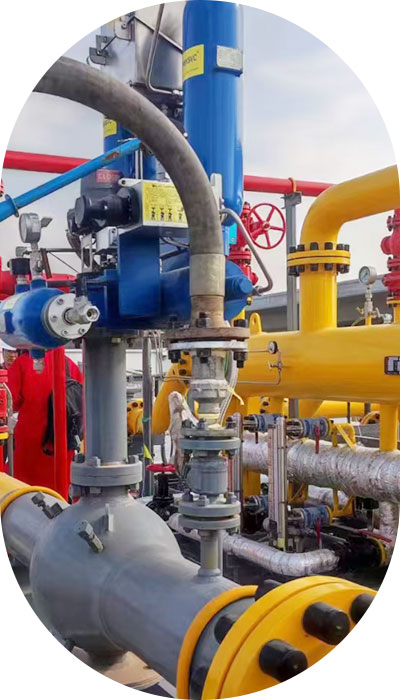


Define the valve’s role, working pressure, temperature, and the type of fluid being controlled.
Identify the pipe diameter and determine the valve’s connection method (flanged, threaded, welded, etc.).
Decide how the valve will be operated, such as manually, electrically, pneumatically, or hydraulically.

Select materials that suit the medium’s pressure, temperature, and corrosiveness, such as carbon steel, stainless steel, or alloy steel.
Choose the specific type of valve (e.g., shut-off, regulating, safety valve) and its design (e.g., gate valve, ball valve, butterfly valve).

For automatic valves, determine the flow resistance, discharge capacity, and the valve’s nominal diameter.
Ensure the valve meets the necessary sealing level based on the application, such as soft or hard sealing.
Validate the valve's performance by simulating its operation under real working conditions, such as pressure, temperature, and flow rates.